- Yokohama-shi Top Page
- Business
- Menu by field
- Architecture and Urban Planning
- Construction-related procedures, laws and regulations, and approvals
- Ordinances and Regulations on Buildings
- About Yokohama standard wave, Yokohama simulated ground motion
- About characteristics of Yokohama simulated ground motion (yoko rock)
The text is from here.
About characteristics of Yokohama simulated ground motion (yoko rock)
Last updated on July 29, 2024.
Basic Approach
- The basic concept for setting seismic motions is as follows.
a For ground motion, the rare ground motion was set to level 1, and the extremely rare ground motion was set to level 2.
Based on the assumption of four earthquakes, the South Kanto Earthquake, the Tokai Earthquake, the Tokyo Earthquake, and the Yokohama Earthquake, the Irikura method is used to estimate the seismic motion waveforms observed in the target area and surrounding areas using the fault model.
The method of Midorikawa-Kobayashi is a semi-experienced method using empirical expressions based on observation data of strong seismic gauges, creating a velocity response spectrum (h = 5%) in the earthquake base (Vs approximately 3.0 km/sec). In addition, the method of "Irikura" is based on similar rules between major earthquake and small earthquakes, and predicts seismic waveforms at major earthquake using the observation waveforms of small earthquakes such as aftershock as element waves. In fact, the fault plane of main shock is divided into small areas, and elemental waves are generated from this small area, taking into account the difference in destruction time and propagation time, the waveform of main shock is created.
c Procedure for setting simulated ground motion
(a) The response spectrum (h = 5%) is calculated from the synthetic wave of "Irikura".
(b) Overlay the response spectrum according to the method of "Midorigawa / Kobayashi" and "Irikura".
(c) (b)Calculate the synergistic mean and standard deviation (σ) of the response spectrum.
(d) Set the proposed spectrum that wraps the response spectrum of the synergy average +1σ.
(e) Create a simulated ground motion that conforms to the proposed spectrum.
d Create simulated seismic waveform
The simulation ground motion waveform was created by Hirasawa and Watabe's "Creation of simulated ground motions that conform to the multivalent target response spectrum."
Application of Yokohama simulated earthquake motion
a Yokohama simulated ground motion was created on the assumption of the base of the Minato Mirai 21 and Shin-Yokohama districts (Vs on the upper surface of the Dotan layer approximately 430 m/sec). Therefore, it can be applied in other districts that show almost the same basic characteristics. It is also expected that the use of simulated ground motions at approximately 150 locations in the "Earthquake Map" formulated by the City of Yokohama, General Affairs Bureau Crisis Management Office will be utilized.
b Yokohama simulated ground motion on the ground surface
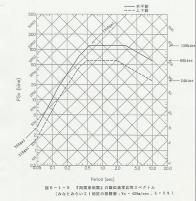
The Yokohama simulated ground motion was assumed to be four earthquakes: the South Kanto Earthquake, the Tokai Earthquake, the Tokyo Earthquake, and the Yokohama Earthquake. Regarding the simulated ground motion of the South Kanto Earthquake, using the ground model of the Minato Mirai 21 district and Shin-Yokohama district, the response calculation using the equivalent linear method of 1D wave theory is performed, and the acceleration waveform of the ground surface and the speed response spectrum are shown, so similar ground models can be used as reference.
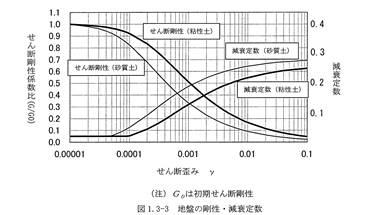
If the ground model is different, the shear rigidity and attenuation constant of the ground as dynamic characteristics of the ground have nonlinear properties that vary depending on the level of shear distortion, so it is necessary to evaluate this effect appropriately during an earthquake. As shown in the figure, as the distortion increases, the rigidity decreases and the attenuation increases. Therefore, it is necessary to note that in major earthquake, it is expected that the ground excellence period will be longer due to a decrease in rigidity due to increased distortion, and in the case of soft ground or ground where there is a risk of liquefaction, buildings with long natural cycles such as high-rise buildings and seismic isolation buildings may have greater response.
In the calculation method of amplification characteristics, the surface ground is assumed to be stratified ground, and is evaluated based on the concept of 1D wave propagation theory, unless there is significant non-stratification. In this case, it is common to calculate by rigidity dependent on the distortion level of the surface ground and equivalent linear analysis using attenuation (SHAKE). If it is determined that it is difficult to replace it with stratospheric ground, it is necessary to model the ground using FEM or the like.
Inquiries to this page
Housing and Architecture Bureau Building Guidance Department, Building Guidance Division
Phone: 045-671-4536
Phone: 045-671-4536
Fax: 045-681-2437
E-Mail address [email protected]
Page ID: 861-721-681


 (Image: 77KB)
(Image: 77KB)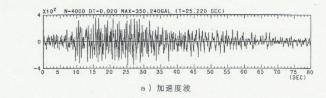 (Image: 15KB)
(Image: 15KB)




