- Yokohama-shi Top Page
- Health, medical care, welfare
- Health, medical care
- Food safety
- Food Safety Yokohama WEB
- Thing about food labeling
- Consumer Information (Nutrition ingredient labeling)
The text is from here.
Consumer Information (Nutrition ingredient labeling)
Have you ever seen food labels? Food labels contain a lot of important information about food. The "Nutrition ingredient labeling" in it allows you to know the amount of nutrients contained in food and is useful for health promotion. Let's use nutrition labeling when choosing food!
Last updated on March 5, 2025.
Let's take advantage of food labeling
This video introduces how to use food labeling! Check it out!
Contents
①What is nutrition labeling?
②Check the amount of salt equivalent to the management of hypertension!
③Let's think about a well-balanced menu even for ready-to-eat meals such as side dishes!
④Let's check how much energy is!
⑤Health food is for supplementing meals?
⑥Prevention of undernutrition in the elderly
⑦Use nutrition highlighting such as "A lot of XX" and "○% cut"
Click here for advertising materials related to nutrition labeling
Food Labeling Quiz-Nutrition Emphasis Edition-
Other food labeling
Health promotion utilizing nutrition ingredients
Let's refer to how the Hamako family uses food labeling.
Hamako's family

①What is nutrition labeling?
About nutrition labeling
Processed foods sold in containers and packaging are required to have the amount and calorific value of nutrients. The five values of calories (energy), protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and salt equivalents are always displayed. The nutrition labeling also shows the amount per food unit, such as 100g, 100ml, and 1 package.
When nutrition labeling can be omitted or labeling is not required.
In some foods, nutrition labeling may be omitted or labeling may not be required.
- Not in containers and packaging
- The display area of containers and packaging is approximately 30 square centimeters or less.
- Alcoholic beverages
- Those with a small degree of contribution as a source of nutrition (tea leaves, spices, etc.)
- Materials whose raw materials are changed in a very short period of time (such as daily lunch boxes)
- Those sold by businesses exempt from the obligation to pay consumption tax under Article 9, Paragraph 1 of the Consumption Tax Law (for the time being, those sold by small businesses prescribed in Article 2, Paragraph 5 of the Basic Act on Small and Medium Enterprises) Including.)
- When a food is manufactured or sold in a place where it is processed.
- When transferring to an unspecified number of persons or a large number of persons
②To manage hypertension, check the amount equivalent to salt.
Amount equivalent to salt
Salt consists of sodium and chlorine. In the nutrition labeling, the formula is "sodium (mg) x 2.54 ÷ 1000 = salt equivalent (g)" and is displayed by converting the sodium content in food to the amount of salt.
Sodium is a mineral that regulates the body's osmotic pressure and is essential to maintain life function, but if taken too much, it can cause diseases such as hypertension and stomach cancer.
Japanese tend to consume more salt than the target daily salt intake. Therefore, it is important to check the amount of salt contained in the food and adjust the intake.

③Let's think about a well-balanced menu even for ready-to-eat meals such as side dishes.
Protein
Protein is a major component of the tissues such as the skeleton and muscles of the human body, and also performs various functions such as adjusting metabolism as a material for enzymes and hormones, and is essential for maintaining life functions and physical activity. It is abundant in meat, fish, eggs, soy products, milk and dairy products, etc.
Lipids
While lipids are an essential energy source for the maintenance of cell membranes, excessive intake increases the risk of obesity and heart disease. It is abundant in fried foods, snacks, and Western sweets that use a lot of fat, oil, margarine, butter, and oil.
Carbohydrates
The most important role of carbohydrates is its function as an energy source. Carbohydrates are divided into carbohydrates and dietary fiber, and carbohydrates become glucose when decomposed in the body. Gaccharides are important tissues because tissues such as the brain and nerve tissue can usually only be used as an energy source. However, if you take too much, it turns into fat in the body and causes obesity. It is abundant in rice, bread, noodles, potatoes, sugar and sweets.
④Let's check how much energy is.
Energy is used for the maintenance of life functions and physical activity. There is no change in weight when the energy intake and consumption are equal. It is important to balance intake and consumption to maintain a desirable BMI for maintaining and improving health and lifestyle-related diseases prevention.
What is BMI?
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height (m) ÷ height (m)
Target BMI
18-49 years old
18.5~24.9 kg /㎡
50-64 years old
20.0~24.9 kg /㎡
65 years old or older
21.5~24.9 kg /㎡
Please refer to the table below for the amount of energy required per day. Let's use about one-third of a day per meal.

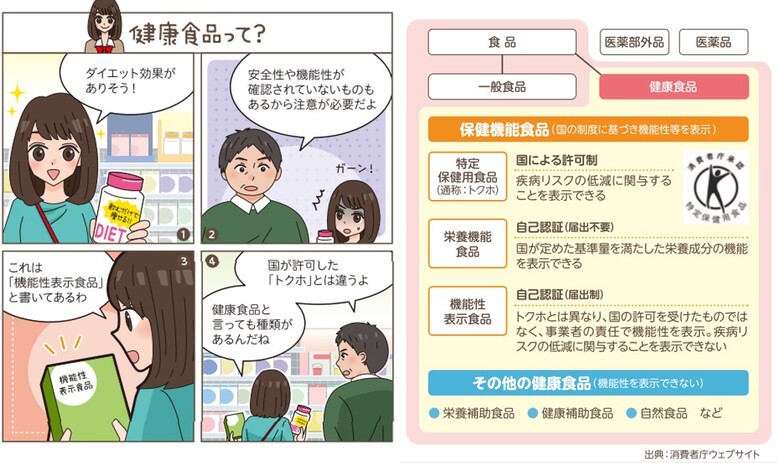
⑤Health foods are for supplementing meals
What we consume from the mouth is divided into food and medicine.
Tablets and capsule-shaped health foods look like drugs, but are "food" and have no effect on cure or prevent disease.
Health foods include health-functional foods that can display functionality based on the national system, and other health foods.
The basics of maintaining and improving health are "nutritiously balanced diet, moderate exercise, and sufficient rest."
When using health foods
◆Check the indication of the estimated intake per day, precautions, etc.
◆If you are taking medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
◆Don't try to solve the uneven diet and disturbances in life with health foods easily, but use it well as an auxiliary one.
⑥Prevention of undernutrition in the elderly

⑦Use nutrition highlighting such as "A lot of XX" and "○% cut"
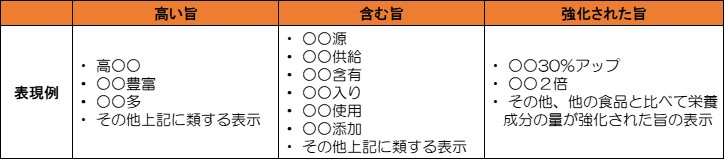
Nutrition emphasis is a sign that the content is higher or less than a certain standard. Those that indicate that the content is higher than a certain standard are indicated as replenishment, and those that indicate that the content is less than a certain standard are indicated as that appropriate intake can be made.
Nutrients that are scarce or overtake can be selected with nutrition highlighting as a landmark. You can check the amount actually contained by looking at the nutritional information label.

Notation that can be replenished
Nutrients that can be described as replenished include protein, dietary fiber, zinc, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, magnesium, niacin, pantotensic acid, biotin, vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12, C, D, E, K and folic acid.
Notation indicating that proper intake is possible
Nutrients that can indicate that proper intake can be made include calories, lipids, saturated fatty acids, cholesterol, sugars, and sodium.

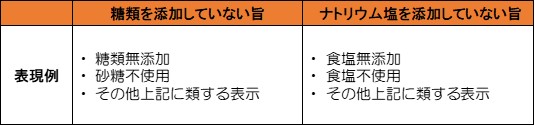
Notation to indicate that it has not been added
Saccharides and sodium salts can be indicated to indicate that they are not added if all of the requirements stipulated by laws and regulations are met.
Advertising materials related to nutrition labeling
Let's utilize food labeling (PDF: 5,918KB)
The Consumer Affairs Agency's website (outside site) also contains information on health promotion utilizing nutrition ingredients.
Food Labeling Quiz-Nutrition Emphasis Edition-

Quiz①
Do you have a numerical standard with plenty of calcium?
Answer①
〇
Commentary①
Nutrition emphasis is a sign that the target nutritional components are higher or less than a certain standard.
If calcium is higher than the standard value, it can be displayed as "rich calcium".

In addition, there are the following types of information.
There are standards for labeling when emphasizing that there are many nutritional components, and standards for labeling when emphasizing that there are few nutritional components, and there are numerical standards for each.

(Source: "Would you like to use nutrition labeling?" Consumer Affairs Agency leaflet (outside site))
Quiz②
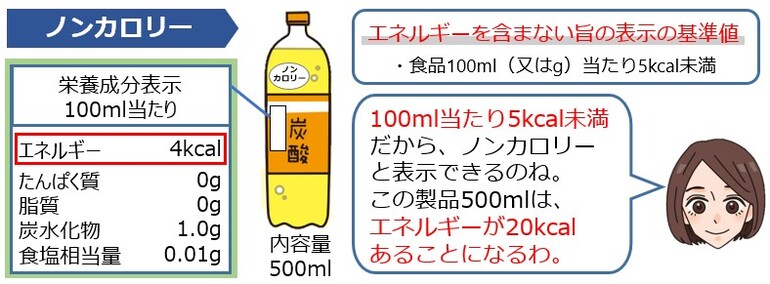
Do you mean non-calories are 0 kilocalories?
Answer②
×
Commentary②
It's not necessarily 0 kilocalories.
If the energy value is below the standard value, it can be displayed as "non-calories".
Other food labeling
Please refer to the Consumer Information (General Food Labeling).
You may need a separate PDF reader to open a PDF file.
If you do not have it, you can download it free of charge from Adobe.
![]() To download Adobe Acrobat Reader DC
To download Adobe Acrobat Reader DC
Inquiries to this page
Food and Hygiene Division, Medical Care Bureau Health and Safety Department
Phone: 045-671-3378
Phone: 045-671-3378
Fax: 045-550-3587
E-Mail address [email protected]
Page ID: 675-220-160